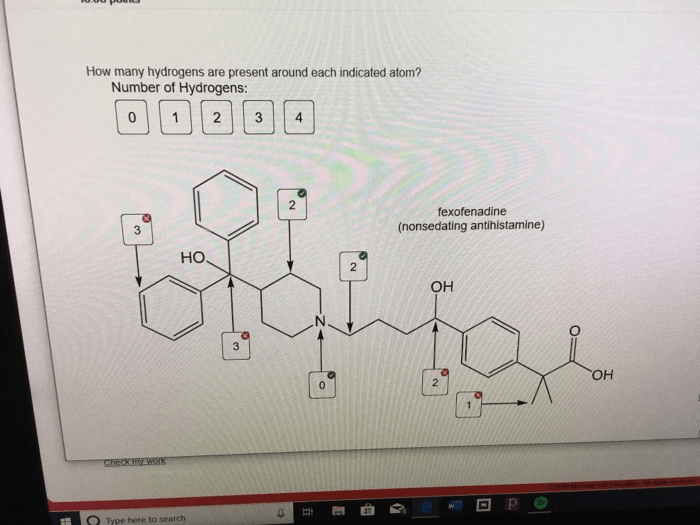
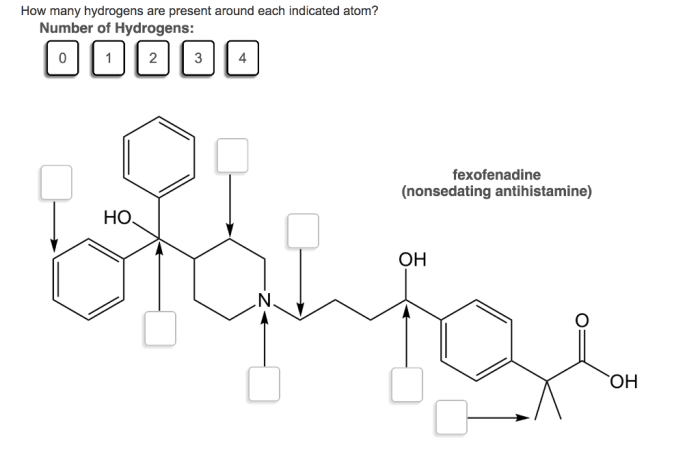
How many hydrogens are present around each indicated atom – The determination of hydrogen count around indicated atoms is a crucial aspect of understanding molecular structure and properties. This comprehensive guide delves into the concept of identifying indicated atoms, the methods for counting hydrogen atoms bonded to them, and the significance of hydrogen count variations in understanding molecular behavior.
By exploring the factors influencing hydrogen count and demonstrating how to represent this information in chemical structures, this guide provides a thorough understanding of the applications of hydrogen count analysis in chemistry. It discusses how hydrogen count information can aid in predicting molecular properties and its use in chemical research and industry.
1. Determining Hydrogen Count Around Indicated Atoms
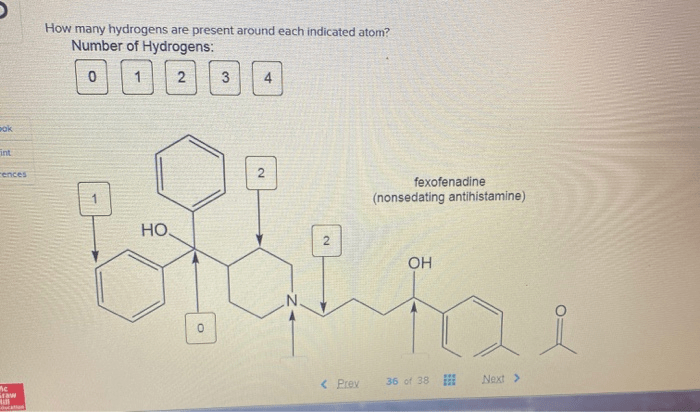
Identifying indicated atoms in a chemical structure involves recognizing specific atoms that are highlighted or designated for further analysis. These indicated atoms can be identified by various notations, such as boldface, italics, or circles around the atom symbol. By understanding the context and conventions of the chemical structure, researchers can determine which atoms are indicated for hydrogen count analysis.
For instance, in the molecule CH 3CH 2OH, the indicated atom is the carbon atom in the methyl group (CH 3). This carbon atom is denoted by a boldface symbol to indicate that its hydrogen count is of interest.
2. Hydrogen Count Variations, How many hydrogens are present around each indicated atom
The number of hydrogen atoms bonded to indicated atoms can vary depending on several factors, including the element type, hybridization, and molecular structure. For example, carbon atoms typically have a maximum of four hydrogen atoms bonded to them, while oxygen atoms can have a maximum of two hydrogen atoms.
Hybridization also affects hydrogen count, as sp 3hybridized carbon atoms can bond with four hydrogen atoms, while sp 2hybridized carbon atoms can bond with three hydrogen atoms.
The molecular structure can also influence hydrogen count. In the molecule CH 3CH 2CH 3, each carbon atom is bonded to three hydrogen atoms. However, in the molecule CH 3CH=CH 2, the carbon atoms in the double bond are bonded to only one hydrogen atom each.
3. Structural Representation
Hydrogen count information can be represented in chemical structures using various methods. One common approach is to use superscripts to indicate the number of hydrogen atoms bonded to each indicated atom. For example, the molecule CH 3CH 2OH can be represented as CH 3CH 2OH 1to indicate that the indicated carbon atom has one hydrogen atom bonded to it.
Another method is to use a table to organize hydrogen count data for multiple indicated atoms. The table can include columns for the indicated atom, the number of hydrogen atoms bonded to it, and any additional relevant information.
4. Applications in Chemistry
Hydrogen count analysis has various applications in chemistry. It can aid in predicting molecular properties, such as polarity and solubility. Polarity is determined by the distribution of electrons in a molecule, and hydrogen atoms can contribute to polarity by creating a dipole moment.
Solubility is influenced by the ability of a molecule to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, and hydrogen count can provide insights into the potential for hydrogen bonding.
Hydrogen count analysis is also used in chemical research and industry. In drug design, for example, hydrogen count information can help researchers understand the interactions between drugs and biological molecules. In the chemical industry, hydrogen count data can be used to optimize reaction conditions and improve product yields.
FAQ Summary: How Many Hydrogens Are Present Around Each Indicated Atom
What is the significance of hydrogen count variations?
Hydrogen count variations can significantly impact molecular properties such as polarity, solubility, and reactivity. Understanding these variations is crucial for predicting molecular behavior and designing molecules with desired properties.
How is hydrogen count information represented in chemical structures?
Hydrogen count information can be represented in chemical structures using explicit hydrogen symbols or implicit hydrogen notation. Explicit hydrogen symbols show each hydrogen atom individually, while implicit hydrogen notation assumes that hydrogen atoms are present to satisfy the valence requirements of the indicated atoms.
What are the applications of hydrogen count analysis in chemistry?
Hydrogen count analysis finds applications in various areas of chemistry, including predicting molecular properties, understanding reaction mechanisms, and designing new materials. It is also used in analytical chemistry to determine the structure and composition of unknown compounds.